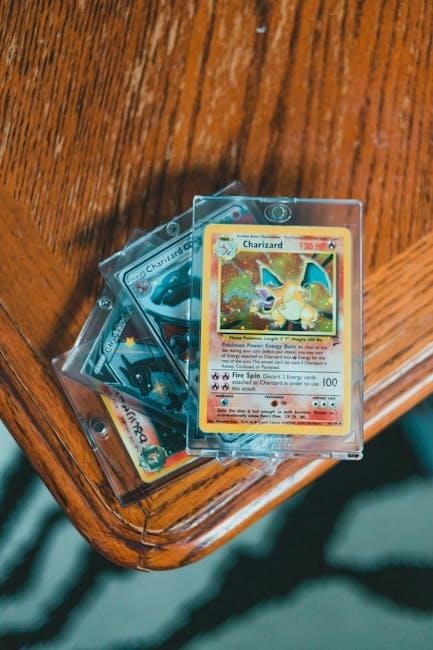
Pokémon fans rejoice! The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide‚ published by VIZ Media‚ is a comprehensive resource detailing Pokémon stats and evolutions.
Initially covering 491 Pokémon‚ later editions expanded to include all 898 up to Generation VIII’s Crown Tundra‚ offering detailed profiles.
These guides‚ often in two volumes‚ present full-color illustrations‚ descriptions‚ Abilities‚ movesets‚ and evolutionary chains for each Pokémon.
Bonus content‚ like posters featuring rare Pokémon‚ further enhances the experience‚ making it a must-have for dedicated trainers and collectors.
It’s a fantastic tool for both newcomers and seasoned players seeking to master the world of Pokémon and complete their Pokédex journey.
What is the Pokémon Pocket Guide?
The Pokémon Pocket Guide‚ primarily published by VIZ Media‚ serves as an exhaustive compendium of Pokémon information‚ designed for enthusiasts of all levels. It’s more than just a list; each entry provides a detailed snapshot of a specific Pokémon‚ encompassing vital statistics and characteristics.
Initially‚ the guide focused on the Pokémon discovered up to a certain generation‚ progressively expanding with each new release. The “Complete” versions aimed to include all known Pokémon at the time of publication‚ reaching 898 with the inclusion of those from Generation VIII and the Crown Tundra expansion.
Presented in a visually appealing format‚ the guide features full-color illustrations alongside descriptive text‚ making it accessible and engaging. It’s a portable resource‚ ideal for referencing during gameplay or simply for deepening one’s knowledge of the Pokémon universe.
History and Editions of the Guide
The Pokémon Pocket Guide evolved alongside the Pokémon franchise itself. Early editions‚ released as the games gained popularity‚ covered a smaller roster of Pokémon‚ reflecting the available creatures at the time. As new generations emerged‚ so too did updated versions of the guide.
VIZ Media became a key publisher‚ releasing “Complete” editions aiming for comprehensive coverage. These often appeared in two-volume sets to accommodate the growing number of Pokémon. Notably‚ initial releases of some editions included bonus content like posters featuring elusive Pokémon such as Shaymin and Arceus.
Reprinted versions sometimes rectified omissions‚ ensuring all Pokémon‚ even those initially excluded‚ were represented. The guide’s history demonstrates a commitment to providing fans with the most up-to-date and complete information available.

Pokémon Entries and Organization
Pokémon entries within The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide are meticulously organized‚ primarily by Pokédex number‚ ensuring a systematic and accessible reference for trainers.
Each entry delivers detailed information‚ including illustrations‚ descriptions‚ stats‚ Abilities‚ and evolution details.
Pokédex Number Organization
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide fundamentally structures its Pokémon entries around the official Pokédex number assigned to each species. This organizational method provides a consistent and easily navigable system for users‚ mirroring the in-game experience of discovering and cataloging Pokémon.
Starting with Bulbasaur at number 001‚ the guide progresses sequentially through each generation‚ presenting Pokémon in the order they were initially revealed. This approach allows trainers to easily track their progress in completing the Pokédex‚ both within the game and within the guide itself.
The Pokédex number serves as a primary identifier‚ facilitating quick lookups and comparisons between different Pokémon. This systematic arrangement is particularly useful for understanding evolutionary relationships and identifying Pokémon within specific regions or generations.
Essentially‚ the guide’s organization reflects the core principle of Pokémon collecting and discovery‚ making it an intuitive and user-friendly resource.
Pokémon Information per Entry
Each Pokémon within The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide receives a dedicated page brimming with essential information for trainers. A vibrant‚ full-color illustration immediately captures the Pokémon’s appearance‚ showcasing its design and unique characteristics.
Following the illustration is a detailed description‚ providing insights into the Pokémon’s behavior‚ habitat‚ and lore. Crucially‚ each entry lists key statistics‚ including base stats‚ Abilities‚ and a selection of learnable moves.
Evolutionary information is prominently featured‚ clearly outlining pre-evolutions and potential further evolutions. This comprehensive approach ensures trainers have all the necessary data to understand and utilize each Pokémon effectively.
The guide aims to be a complete reference‚ offering a snapshot of each Pokémon’s strengths‚ weaknesses‚ and overall role within the Pokémon world.
Pokémon Illustration and Design
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide places significant emphasis on visual representation‚ featuring full-color illustrations for every Pokémon. These aren’t merely depictions; they showcase the artistry and design philosophy behind each creature.
Illustrations aim to capture the essence of each Pokémon‚ highlighting its unique features and personality. The quality of these images is consistently high‚ providing a visually appealing experience for collectors and fans.
The design choices‚ from color palettes to pose selection‚ contribute to a deeper understanding of the Pokémon’s characteristics and role within its ecosystem.
These illustrations serve not only as aesthetic elements but also as crucial reference points for identification and appreciation of the creative design work invested in the Pokémon franchise.
Detailed Pokémon Descriptions
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide doesn’t just show you the Pokémon; it tells you about them. Each entry includes a detailed description‚ offering insights into the creature’s behavior‚ habitat‚ and lore.
These descriptions go beyond simple physical attributes‚ delving into the Pokémon’s origins‚ cultural significance within the Pokémon world‚ and any unique characteristics that set it apart.
The writing style is accessible to a wide audience‚ making it enjoyable for both casual fans and dedicated players. These narratives enrich the overall experience‚ fostering a deeper connection with each Pokémon.
Information provided helps trainers understand a Pokémon’s strengths‚ weaknesses‚ and potential role in a team‚ enhancing strategic gameplay and overall enjoyment of the franchise.
Key Statistics and Data
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide provides crucial statistical data for each Pokémon‚ essential for competitive battling and team building. This includes base stats for HP‚ Attack‚ Defense‚ Special Attack‚ Special Defense‚ and Speed.
Beyond base stats‚ the guide lists a Pokémon’s potential moves‚ detailing their type‚ power‚ accuracy‚ and effects; This information is vital for strategizing and maximizing a Pokémon’s combat potential.
Furthermore‚ the guide clearly outlines each Pokémon’s Abilities‚ explaining their effects and how they can influence battles. This data empowers trainers to make informed decisions.
Presented in a concise and easily digestible format‚ these key statistics and data points are invaluable resources for any serious Pokémon trainer seeking to optimize their team.

Pokémon Stats and Abilities
Pokémon stats—HP‚ Attack‚ Defense‚ and more—define battle prowess‚ while Abilities offer unique tactical advantages‚ detailed within The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide.
Understanding Pokémon Stats
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide meticulously details each Pokémon’s core statistics‚ crucial for competitive battling and team building. These stats – HP (Hit Points)‚ Attack‚ Defense‚ Special Attack‚ Special Defense‚ and Speed – numerically represent a Pokémon’s capabilities.
HP dictates survivability‚ while Attack and Special Attack determine offensive power; Defense and Special Defense mitigate incoming damage. Speed governs turn order in battle.
Understanding how these stats interact is paramount. A Pokémon with high Attack but low Speed might be outpaced by a faster opponent. The guide provides these values‚ allowing trainers to strategically assess strengths and weaknesses.
These stats aren’t static; they increase with leveling up and can be further influenced by natures‚ EVs (Effort Values)‚ and IVs (Individual Values)‚ adding layers of depth for dedicated players.
Pokémon Abilities Explained
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide doesn’t just list stats; it thoroughly explains each Pokémon’s unique Abilities‚ a defining characteristic impacting battle strategy. Abilities are passive effects that trigger under specific conditions‚ offering tactical advantages.
These range from stat boosts (like Keen Eye preventing stat reduction) to altering move effects (like Torrent increasing Water-type move power when HP is low). The guide clearly describes each Ability’s function.
Understanding Abilities is vital for team composition and predicting opponent actions. Some Abilities counter specific strategies‚ while others synergize with certain movesets.
Hidden Abilities‚ also detailed in the guide‚ add another layer of complexity‚ offering alternative strategic options for experienced trainers. Mastering Abilities is key to competitive success.
Movesets and Learnable Moves
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide provides a crucial overview of each Pokémon’s movesets‚ detailing the moves they can learn and at what levels. This information is essential for effective battle preparation and strategic team building.
The guide lists a selection of moves‚ categorized by type‚ showcasing the breadth of offensive and support options available. It highlights both commonly learned moves and those requiring specific methods like TMs or breeding.
Understanding move compatibility allows trainers to optimize their Pokémon’s potential‚ creating synergistic combinations and covering type weaknesses.
The guide’s move listings empower players to tailor their team to counter specific opponents and dominate the battlefield‚ maximizing their chances of victory.

Evolutionary Information
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide meticulously details evolution chains‚ methods‚ and regional forms‚ showcasing pre-evolutions and further evolutions for each Pokémon.
It clarifies how and when Pokémon transform‚ aiding trainers in completing their Pokédex and building powerful teams through strategic evolution.
Evolution Chains and Methods
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide provides a clear and concise breakdown of each Pokémon’s evolutionary path. It doesn’t just list the evolutions; it details how they occur.
Trainers can find information on evolutions triggered by leveling up‚ using specific evolution stones (like Fire Stone or Water Stone)‚ trading with other players‚ or even through unique conditions like happiness or time of day.
The guide meticulously maps out multi-stage evolution chains‚ showing the progression from a basic form to its final‚ most powerful state. For example‚ it clearly illustrates how Charmander evolves into Charmeleon‚ and then into Charizard.
Understanding these methods is crucial for any trainer aiming to build a competitive team or simply complete their Pokédex collection‚ and the guide serves as an invaluable resource.
Pre-Evolutions and Further Evolutions
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide doesn’t simply stop at listing evolutions; it comprehensively covers both pre-evolutions and potential further evolutions for each Pokémon.
For Pokémon with multiple stages‚ the guide clearly outlines the entire lineage‚ tracing back to the earliest form and projecting forward to the final evolved state. This is particularly helpful for understanding complex evolutionary trees.
It highlights any branching evolution paths‚ where a Pokémon might evolve into different forms depending on specific conditions. This allows trainers to make informed decisions about their team’s development.
The guide’s detailed approach ensures that players can fully grasp the potential of each Pokémon and strategically plan their evolutionary journey for optimal results.
Regional Forms and Variations
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide acknowledges the fascinating phenomenon of Regional Forms‚ showcasing how Pokémon adapt and differ across various regions of the Pokémon world.
These variations‚ like Alolan or Galarian forms‚ aren’t merely cosmetic changes; they often include altered typings‚ Abilities‚ and stats‚ significantly impacting battle strategies.
The guide meticulously details these regional differences‚ providing a clear comparison between the standard form and its regional counterpart. This allows trainers to understand the unique strengths and weaknesses of each variation.
By including this information‚ the guide demonstrates a commitment to comprehensive coverage‚ ensuring players are aware of all available Pokémon forms and their strategic implications.

Generational Coverage
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide meticulously documents Pokémon across all generations‚ starting with the original 151 and extending through Generation VIII’s Crown Tundra content.
Each edition expands to include newly discovered Pokémon‚ ensuring a continually updated and comprehensive reference for dedicated trainers and collectors.
Original 151 Pokémon
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide dedicates significant coverage to the foundational 151 Pokémon from the Kanto region‚ representing the genesis of the franchise. Each entry provides a detailed illustration‚ capturing the iconic designs that captivated a generation of players.
Beyond visuals‚ the guide offers comprehensive descriptions outlining each Pokémon’s characteristics‚ habitat‚ and lore‚ enriching the understanding of these original creatures. Crucially‚ it lists key statistics‚ including base stats‚ type matchups‚ and learnable moves‚ aiding strategic gameplay.
Evolutionary information is clearly presented‚ detailing pre-evolutions and further evolutions‚ allowing trainers to chart their Pokémon’s growth. This foundational coverage establishes a strong base for understanding subsequent generations and the broader Pokémon universe.
The guide’s meticulous approach to these initial Pokémon demonstrates its commitment to providing a complete and accessible resource for all fans.
Generation II Pokémon (Gold & Silver)
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide expands its coverage with the introduction of the 100 new Pokémon from the Johto region‚ featured in Pokémon Gold & Silver. These entries maintain the guide’s consistent format‚ offering detailed illustrations showcasing the new designs and a comprehensive overview of each creature.
Detailed descriptions delve into their unique characteristics and lore‚ while key statistics provide valuable insights for battle strategy. The guide meticulously outlines their type matchups and available movesets‚ crucial for competitive play.
Crucially‚ the guide clearly illustrates the evolution chains for these Pokémon‚ including branching evolutions and new methods introduced in Generation II. This expansion solidifies the guide’s role as a definitive resource for trainers navigating the expanded Pokémon world.
Generation III Pokémon (Ruby & Sapphire)
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide continues its comprehensive catalog with the addition of the 135 Pokémon debuting in Pokémon Ruby & Sapphire. The guide maintains its established format‚ presenting each new Pokémon with vibrant‚ full-color illustrations and detailed descriptive text.
Information extends to crucial battle statistics‚ including base stats and learnable moves‚ aiding trainers in strategic team building. The guide meticulously details the Abilities introduced in Generation III‚ explaining their effects and tactical applications;
Evolutionary chains are clearly mapped‚ showcasing new evolution methods and branching paths. This expansion further cements the guide’s position as an essential resource for mastering the Hoenn region’s diverse Pokémon roster and competitive battling.
Generation IV Pokémon (Diamond & Pearl)
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide expands its coverage to include the 107 new Pokémon introduced in Pokémon Diamond & Pearl. Consistent with previous editions‚ each entry features a full-color illustration alongside a detailed description of the Pokémon’s characteristics and lore.
The guide provides essential data for competitive play‚ listing base stats‚ available moves‚ and the newly introduced Abilities. It clearly outlines the evolution methods for these Pokémon‚ including those utilizing new items and conditions.
Trainers can leverage this information to optimize their teams and effectively navigate the Sinnoh region. The guide’s continued dedication to comprehensive data makes it invaluable for both casual fans and dedicated competitive players.
Generation V Pokémon (Black & White)
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide meticulously documents the 156 Pokémon debuting in Pokémon Black & White. Each Pokémon receives a dedicated page‚ showcasing vibrant illustrations and in-depth descriptions of their unique traits and origins within the Unova region.
The guide provides crucial statistical data‚ including base stats‚ potential movesets‚ and the intricacies of their Abilities‚ aiding trainers in strategic team building. It details the evolution requirements for these Pokémon‚ including new methods introduced in this generation.
This comprehensive coverage ensures players have the resources to effectively explore Unova and master the challenges presented by this new wave of Pokémon.

Generation VI Pokémon (X & Y)
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide expands its coverage to include the 72 Pokémon introduced in Pokémon X & Y‚ set in the Kalos region. Each entry features detailed illustrations capturing the aesthetic of this generation‚ alongside comprehensive descriptions of their lore and characteristics.
Crucially‚ the guide outlines the new Mega Evolution phenomenon‚ detailing the stat boosts and Ability changes for Pokémon capable of Mega Evolving. It also provides extensive data on their Abilities‚ movesets‚ and evolutionary paths.
This information empowers trainers to strategically utilize these powerful forms and navigate the challenges of the Kalos region effectively.

Generation VII Pokémon (Sun & Moon)
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide meticulously documents the 88 new Pokémon debuting in Pokémon Sun & Moon‚ hailing from the Alola region. Entries showcase vibrant illustrations reflecting the tropical setting and unique designs of these Pokémon.
A key feature is the detailed explanation of Alolan Forms – regional variants with altered typings‚ Abilities‚ and appearances. The guide clarifies these changes‚ aiding trainers in understanding their strategic implications.
Furthermore‚ it provides comprehensive data on Z-Moves‚ powerful attacks unique to Alola‚ including compatible Pokémon and move combinations‚ enhancing battle preparation.
Generation VIII Pokémon (Sword & Shield) & The Crown Tundra
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide’s expanded editions fully encompass the 898 Pokémon discovered through Pokémon Sword & Shield‚ including the additions from The Crown Tundra DLC. Detailed entries cover the Galarian Forms‚ showcasing their distinct appearances and altered stats.
The guide provides crucial information on Dynamaxing and Gigantamaxing‚ explaining how these temporary transformations impact battles and which Pokémon can Gigantamax.
It also meticulously details the Legendary Pokémon introduced in The Crown Tundra‚ alongside their lore and battle strategies‚ offering a complete reference for trainers exploring the Galar region and beyond.

Special Features and Extras
Pokémon Pocket Guides often include bonus posters featuring elusive Pokémon like Shaymin and Arceus‚ enhancing the collector’s value and appeal.
Reprinted editions sometimes feature updated content‚ ensuring the guide remains current with the latest Pokémon discoveries and information.
Included Posters and Leaflets
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide frequently elevates the collector’s experience with exclusive bonus materials‚ most notably double-sided posters and leaflets.
Early editions‚ covering up to 491 Pokémon‚ often included a poster showcasing the then-newly revealed Mythical Pokémon‚ Shaymin‚ on one side and Arceus on the other.
These posters weren’t simply promotional items; they provided crucial information on these rare Pokémon‚ as their full entries weren’t initially included within the main guide itself.
Later reprints and revised editions continued this tradition‚ sometimes updating the included posters to reflect the latest Pokémon additions and discoveries.
These leaflets and posters became highly sought-after collectibles‚ adding significant value to the overall Pokémon Pocket Guide package for enthusiasts.
Bonus Content and Collectibles
Beyond the core Pokémon data‚ The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide series offered various bonus content‚ enhancing its appeal as a collectible item.
The inclusion of double-sided posters‚ featuring elusive Pokémon like Shaymin and Arceus‚ immediately elevated the guide’s desirability among fans.
These posters weren’t merely aesthetic additions; they provided essential information on Pokémon not fully detailed within the main guide’s pages.
The two-volume format itself contributed to the collectible aspect‚ encouraging completionists to acquire both parts for a comprehensive resource.
First edition prints and those with pristine posters often command higher prices in the secondary market‚ solidifying the guide’s status as a valuable collectible.
Guide Updates and Revisions
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide underwent several updates and revisions to remain current with the ever-expanding Pokémon universe.
Initial editions‚ covering up to Generation IV‚ were later expanded with new volumes to encompass Generations V‚ VI‚ VII‚ and ultimately‚ VIII with the Crown Tundra content.
These revisions weren’t simply additions; they involved a complete overhaul‚ bringing the total Pokémon count to 898 across two volumes.
The guides were fully re-illustrated and updated with the latest information on Abilities‚ moves‚ and evolutionary methods for each Pokémon.
This commitment to accuracy and comprehensiveness ensured the guide remained a valuable resource for trainers navigating the evolving landscape of Pokémon battles and collection.

Using the Guide for Gameplay
The Pokémon Pocket Guide empowers players with strategic insights for team building‚ battle preparation‚ and efficient Pokédex completion.

Detailed stats and move lists aid in crafting effective teams and anticipating opponent strategies‚ enhancing the overall gameplay experience.
Team Building Strategies
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide is invaluable for constructing a balanced and competitive team. Utilizing the detailed stat breakdowns‚ trainers can identify Pokémon excelling in Attack‚ Defense‚ Speed‚ and Special stats.
Understanding type matchups‚ readily available within the guide‚ is crucial for creating synergy and exploiting weaknesses. Consider including Pokémon with diverse movepools to cover a broad range of opponents.
The guide’s information on Abilities allows for strategic team compositions‚ capitalizing on effects like Intimidate or Levitate. Don’t overlook potential evolution chains; a seemingly weak Pokémon might transform into a powerhouse!
Finally‚ referencing the guide’s move lists helps select optimal movesets‚ maximizing each Pokémon’s potential and ensuring a well-rounded‚ formidable team.
Battle Preparation and Tactics
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide empowers trainers with the knowledge for effective battle preparation. Before engaging‚ meticulously review your opponent’s potential Pokémon and movesets using the guide’s comprehensive data.
Understanding a Pokémon’s Abilities is paramount; anticipate their effects and formulate counter-strategies. Leverage type advantages identified within the guide to inflict super-effective damage.
Carefully select your team’s moves‚ considering coverage and potential status conditions. The guide’s move descriptions detail effects‚ aiding in strategic decision-making.
During battle‚ adapt to your opponent’s tactics‚ switching Pokémon to exploit weaknesses and maintain momentum. Utilize the guide’s stats to predict damage output and ensure victory!
Completing the Pokédex
The Complete Pokémon Pocket Guide is an invaluable asset for aspiring Pokédex completionists. Its organized layout‚ by Pokédex number‚ streamlines the tracking process across all generations.
Each entry provides crucial information – location data (though not explicitly detailed in the guide itself‚ it complements external resources)‚ evolution methods‚ and regional variations – essential for locating and acquiring each Pokémon.
The guide’s comprehensive coverage‚ up to 898 Pokémon‚ ensures no creature is overlooked. Utilize the illustrations to confirm accurate identification during encounters.
Cross-referencing with in-game data and online resources‚ alongside the guide‚ accelerates your journey to becoming a true Pokémon Master!